Acute viral hepatitis and other viral infections:
Hepatitis A:
Characterestics:
Hepatitis A Older name: infectiuos hepatitis
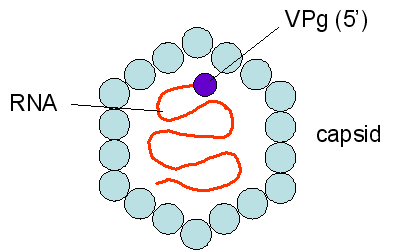
Virus type: RNA
Virus size: 27nm
Incubation period: 15 to 50 days Transmission : fecal-oral
Vertical transmission to fetus: not observed
Serologic diagnosis: Hepatitis A antibody IgM, IgG types
Maximum infectivity in : Prodromal stage
Carrier state: None
Acute clinical forms: Asymtomatic to fulminant
Chronic clinical forms: None
The clinical syndrome of acute HAV infection consists of vague flu-like symptoms with fatigue, weakness, nausea and loss of appetite.
The onset is usually abrupt.
A variety of extrahepatic manifestations including myalgia, arthralgias, arthritis, and urticaria, may occur.
Other forms of HAV infection include cholestatic hepatitis, with a prolonged course marked by itching and jaundice.
The characteristic changes in liver function test findings include marked elevations in AST and ALT.
Most often, these reach levels of 1000 to 2000 U during the early part of the infection.
Elevations in bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase also occur but are more unpredictable.
There is substantial evidence that pregnancy does not alter the course of HAV infection.
However, a higher incidence of fulminant disease during pregnancy has been reported in developing nations.
Concurrent malnutrition has been a suspected cause.
If the course of HAV infection is severe, it may precipitate premature labor in women in the third trimester of pregnancy.
There is no evidence that HAV causes birth defects. Hospitalization may be indicated, specially during the last trimester and in the presence of severe anorexia, nausea, and vomiting.
In rare circumstances in which the mother has acute HAV infection at the time of delivery, immune serum globulin may be administered to the infant.
Even under these conditions, the risk of transmission to the infant seems very small.
Hepatitis A:
Characterestics:
Hepatitis A Older name: infectiuos hepatitis
Virus type: RNA
Virus size: 27nm
Incubation period: 15 to 50 days Transmission : fecal-oral
Vertical transmission to fetus: not observed
Serologic diagnosis: Hepatitis A antibody IgM, IgG types
Maximum infectivity in : Prodromal stage
Carrier state: None
Acute clinical forms: Asymtomatic to fulminant
Chronic clinical forms: None
The clinical syndrome of acute HAV infection consists of vague flu-like symptoms with fatigue, weakness, nausea and loss of appetite.
The onset is usually abrupt.
A variety of extrahepatic manifestations including myalgia, arthralgias, arthritis, and urticaria, may occur.
Other forms of HAV infection include cholestatic hepatitis, with a prolonged course marked by itching and jaundice.
The characteristic changes in liver function test findings include marked elevations in AST and ALT.
Most often, these reach levels of 1000 to 2000 U during the early part of the infection.
Elevations in bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase also occur but are more unpredictable.
There is substantial evidence that pregnancy does not alter the course of HAV infection.
However, a higher incidence of fulminant disease during pregnancy has been reported in developing nations.
Concurrent malnutrition has been a suspected cause.
If the course of HAV infection is severe, it may precipitate premature labor in women in the third trimester of pregnancy.
There is no evidence that HAV causes birth defects. Hospitalization may be indicated, specially during the last trimester and in the presence of severe anorexia, nausea, and vomiting.
In rare circumstances in which the mother has acute HAV infection at the time of delivery, immune serum globulin may be administered to the infant.
Even under these conditions, the risk of transmission to the infant seems very small.

No comments:
Post a Comment